Time for another article from the extensive TetZoo archives, this time a piece from ver 2, 2008 (original here). We begin with this interesting photo provided by my good friend Markus Bühler (of Bestiarium): it shows a bull Asian elephant Elephas maximus at Hagenbeck Zoo, Hamburg…
Domestic Horses of Africa
I’ve written a fair amount about HORSES at TetZoo, predominantly at versions 2 and 3. For reasons, I now aim to reproduce it here at ver 3. We start with a article I first published in 2015 (original version here)…
Hartebeest, Long-Faced Antelopes of Many Forms
In another effort to rescue old TetZoo material from the vandalized archives of ver 2 and 3, here’s a slightly revamped version of a 2009 article on hartebeest (the original version is here)…
Suddenly -- Duikers!
Meeting the Hayling Island Jungle cat
Once again I’m giving you something from the archives, since there’s just no chance at all to produce anything new right now. Here, then, is a TetZoo ver 3 article that was originally published there in 2013 (that version is here). Ironically, that 2013 article was itself a republishing of a version from 2009…
The Incredible South American Maned Wolf
Inspired by my recent article on South American wild dogs, I went to the trouble of digging out a very brief TetZoo ver 2 article I published in 2007 on the remarkable and beautiful 'fox on stilts', the Maned wolf Chrysocyon brachyurus (said article is here). My aim was to augment and update that text such that it might be a useful one-stop review on this animal.
Kogia, Shark-Mouthed Horror
Once more I must resort to plundering stuff from the archives, this time an article from TetZoo ver 2, originally published in July 2008 (and available here at wayback machine). Today: the kogiid sperm whales!
Conservation Concerns for South America's Remarkable Endemic Dogs, Revisited for 2022
Greater Noctules: Specialist Predators of Migrating Passerines, Revisited
For reasons, I still have no time at all for blogging, alas. And thus I once again give you an article from the archives. This time, one of my favourite BAT articles. I’ve covered bats a fair bit at TetZoo (see below for links), but this remains one of the most memorable (it has received some minor updates relative to its initial outing, which occurred here in 2006 at ver 1)…
Release the Fossil Pronghorns!!
Here we are with another effort to recycle material from the TetZoo archives (and invariably ruined by its hosters and hence made unavailable to those who might consult it). This time: a revamped version of my fossils pronghorns article, first published at ver 2 back in 2010 (an original is here)…
Santa Cruz’s Duck-Billed Elephant Monster, Definitively Identified
You Have Your Giant Fossil Rabbit Neck All Wrong, Redux
Ross Barnett’s 2019 The Missing Lynx: the Past and Future of Britain’s Lost Mammals
The Hunt for Persisting Thylacines, an Interview
Predation and Corpse-Eating in Armadillos
Why the World Has to Ignore David Peters and ReptileEvolution.com
The Shrews of the World
Cloudrunners and Other Cloud Rats of the Philippines
I’ve surely said on several occasions over the years that I’ve never written enough about rodents here at TetZoo. But, then, you could write about nothing BUT rodents and still not write about them enough… there are just so many of them, both in terms of numbers of species and individuals. Whatever, I’ve opted today to write about cloudrunners and other cloud rats, a group of luxuriantly furred, large, striking members of Muridae – the rat and mouse family – endemic to the Philippines.
Stop Saying That There Are Too Many Sauropod Dinosaurs, Part 2
A few authors would have it that there are too many damn dinosaurs (TMDD!): that the rich sauropod assemblage of the Late Jurassic Morrison Formation of the continental western interior of the USA simply contains too many species, and that we need to wield the synonymy hammer and whack them down to some lower number. In this article and those that follow it, I’m going to argue that this view is naïve and misguided. You’ll need to have read Part 1 – the introduction – to make sense of what follows here. Ok, to business…
Extreme Cetaceans, Part 3
Hello faithful and noble readers. Recall the unfinished series on EXTREME CETACEANS? Today we continue with the next episode in said series.
Caption: Stenella longirostris, Phocoena dioptrica and Sousa chinensis, three of the cetacean species covered in the previous parts of this series. Image: Darren Naish.
If you don’t know what the deal is here, it’s that I’m writing about those cetaceans which I consider ‘extreme’, this meaning that they’re “weird, possessing anatomical specialisations and peculiarities that are counter-intuitive and little discussed, and most likely related to an unusual ecology, physiological regime, feeding strategy or social or sexual life”, to quote the first article in the series. And thus we get on with it…
Right whale dolphins. Many dolphin species are aesthetically pleasing because they’re of a beautifully streamlined, attenuate shape, and because they have clean, tidy colour schemes where contrasting blocks of colour are neatly separated, and sometimes augmented or marked by parallel, sweeping lines. This combination – an attenuate, streamlined form and a tidy, well-demarcated colour scheme – is carried to an extreme in the two Lissodelphis species, or right whale dolphins.
Caption: Alcide Dessalines d'Orbigny’s 1847 illustration of the Southern right whale dolphin Lissodelphis peronii. The species is named for naturalist François Peron, the first European to report a sighting of this species. Image: public domain (original here).
Right whale dolphins are mid-sized as dolphins go (about 2-3 m long), short-beaked, and incredibly attenuate. Their pectoral flippers and tail flukes are small, a dorsal fin is absent, and the tailstock tapers to a ridiculous degree. They also have the flashiest, tidiest colour scheme of black and white. They look nothing like the enormous, super-bulky right whales, but do resemble them in lacking a dorsal fin. They’re also incredibly fast, among the fastest of all cetaceans,
Caption: a Southern right whale dolphin group, photographed in 2008. These dolphins are often seen in large groups of 100 individuals or more. Image: Lieutenant Elizabeth Crapo, NOAA Corp, public domain (original here).
Right whale dolphins, incidentally, are close kin of lags (the Lagenorhynchus and Sagmatias dolphins) and probably of the small, short-beaked Cephalorhynchus dolphins (the most familiar of which is the piebald Commerson’s dolphin C. commersoni) (McGowen et al. 2009). But in my headcanon they’re either miniaturised, late-surviving basilosaurids, or whale-mimicking, fully aquatic penguins that have time-travelled from the Dixonian Era to the present. Look at the pictures here and you’ll see what I mean.
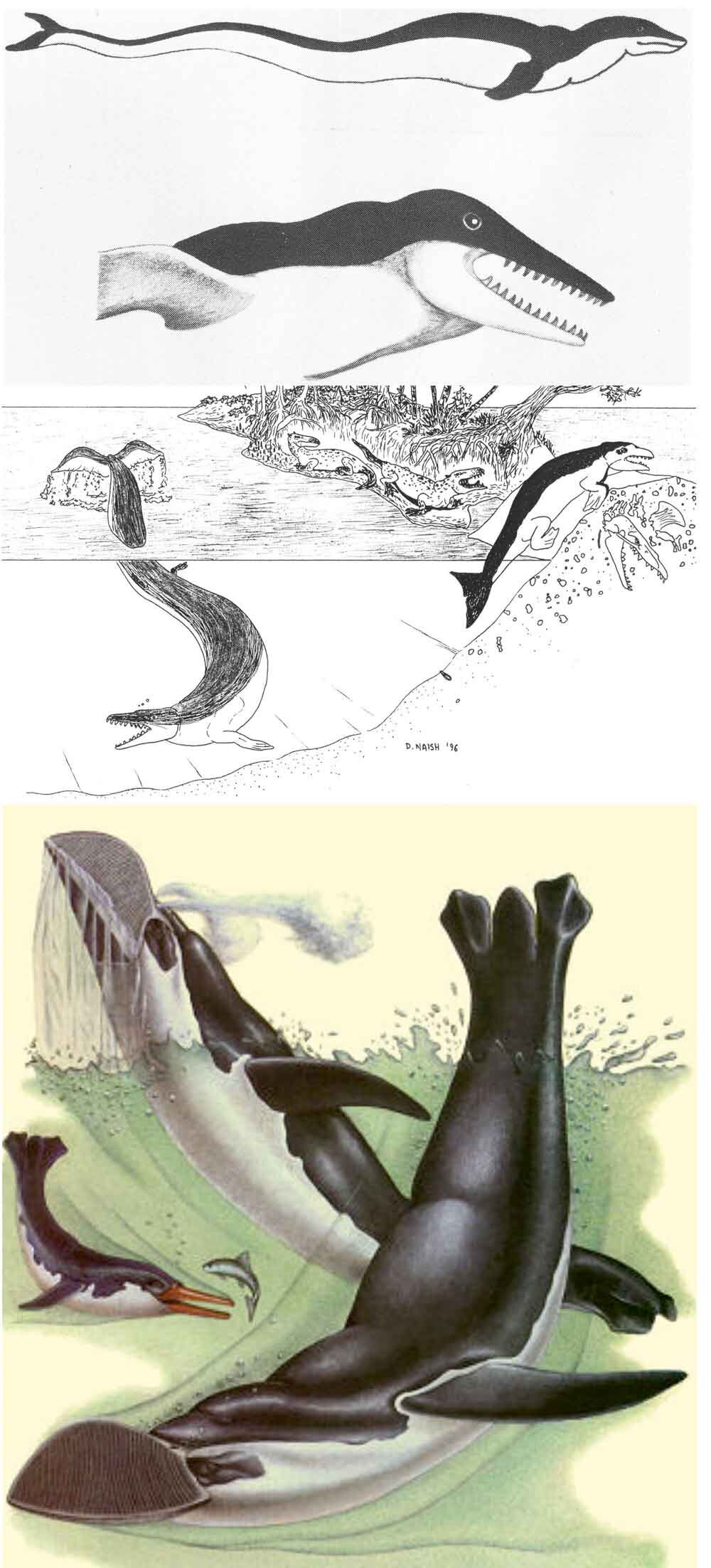
Caption: old depictions of basilosaurs and other archaeocetes – those at top are from McEwan (1978) and Naish (1996) – reveal that right whale dolphins are actually descendants of a lineage outside of Neoceti. Or perhaps they’re future penguins, like the Vortex (from Dixon 1981). Images: McEwan (1978) and Naish (1996), Dixon (1981).
The Pesut. In 1989, I thought I knew all the extant cetacean species known to science at the time. So I was blown away when the Today newspaper, which I used to read, ran a two-page feature on a very odd cetacean which was touted as “the only new breed to be discovered in thirty-four years”, this being a reference to the number of years that had elapsed since the scientific naming of Fraser’s dolphin Lagenodelphis hosei in 1956. Evidently, the article was reporting a proposal – seemingly originating with Francois-Xavier Pelletier – in which the cetacean concerned was being considered a potential new species. Grey, toothless and prone to squirting jets of water for fun, it was said to be a freshwater inhabitant of Borneo’s Mahakam River, and was dubbed the Pesut. The what?
Caption: a Today newspaper article of 1989 reports ‘the Pesut’ as a new kind of dolphin. I regret that I don’t have the complete citation for this article; in my wisdom I clipped the date and other details at some point. Readers with exceptional memories might recognise the photo at upper right as the inspiration for a SpecZoo-themed piece of art…
Today, the Pesut isn’t regarded as a distinct species, but a local variant of the Irrawaddy dolphin Orcaella brevirostris. It’s known locally as the Pesut Mahakam, more formally as the Mahakam River dolphin, and is seemingly – with the rest of the Orcaella dolphins – an early-diverging member of the globicephaline clade (McGowen et al. 2009, Vilstrup et al. 2011), otherwise known for including killer whales, pilot whales and kin, the ‘blackfish’ [UPDATE: killer whales no longer appear to be part of Globicephalinae; see comments]. Pelletier’s proposal that the Mahakam River Orcaella population might be distinct is odd, since anyone familiar with the historical taxonomy of Orcaella knows (or should have known, even in 1989) that Pesut Mahakam is a local name for some riverine populatons of O. brevirostris (Marsh et al. 1989). Furthermore, there’s a long history of riverine Orcaella populations being considered distinct and of having their taxonomic status tested and re-evaluated.
Caption: an Irrawaddy dolphin photographed in Cambodia. Image: Stefan Brending, CC BY-SA 3.0 (original here).
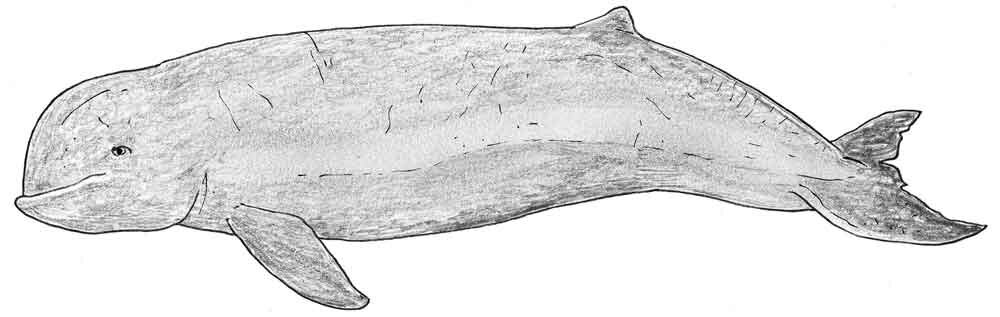
Whatever, the Pesut does look kinda unusual. Books on whales very often say or imply that the Boto or Amazon river dolphin Inia geoffrensis and Beluga Delphinapterus leucas are the only two living cetaceans with an especially mobile neck, but this very probably isn’t true and Pesuts are often shown with the head being held at an obvious angle relative to the body. Other weird features that make the Pesut ‘extreme’ are its globular, short-snouted face and smiling mouthline, and the crease that runs along part of its dorsal midline.
Caption: an effort to portray an Irrawaddy dolphin in life. This dolphin can reach 2.75 m in length, males being larger. Image: Darren Naish.
If you know anything about cetaceans you’ll be aware of the fact that the Irrawaddy dolphin is superficially similar to the Beluga, and it’s this similarity which has led to the occasional suggestion that Orcaella might not be a dolphin but a tropical member of the same family as the Beluga (Monodontidae). This isn’t a ridiculous idea, but it isn’t supported by the detailed anatomy of this animal, or by molecular data.
Caption: I said the montage would become increasingly cluttered. And we’re not done yet. Image: Darren Naish.
And that’s where we’ll end things for now; the next article in the series will appear soon. And I’ll publish a lot more on whales here in the future. Here’s some of the stuff that exists in the archives (as always, much of the material at TetZoo versions 2 and 3 has been ruined by the removal of images, so I’m linking to wayback machine versions)…
A 6 ton model, and a baby that puts on 90 kg a day: rorquals part I, October 2006
From cigar to elongated, bloated tadpole: rorquals part II, October 2006
Lunging is expensive, jaws can be noisy, and what’s with the asymmetry? Rorquals part III, October 2006
On identifying a dolphin skull, July 2008
Seriously frickin' weird cetacean skulls: Kogia, shark-mouthed horror, July 2008
Scaphokogia!, July 2008
Cetacean Heresies: How the Chromatic Truthometer Busts the Monochromatic Paradigm, April 2015
Whale Watching in the Bay of Biscay, August 2019
Extreme Cetaceans, Part 1, September 2019
Extreme Cetaceans, Part 2, September 2019
Refs - -
Dixon, D. 1981. After Man: A Zoology of the Future. Granada, London.
Marsh, H., Lloze, R., Heinsohn, G. E. & Kasuya, T. 1989. Irrawady dolphin Orcaella brevirostris (Gray, 1866). In Ridgway, S. H. & Harrison, R. (eds) Handbook of Marine Mammals Volume 4. Academic Press (London), pp. 101-118.
McGowen, M. R., Spaulding, M., Gatesy, J. 2009. Divergence date estimation and a comprehensive molecular tree of extant cetaceans. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 53, 891-906.
Naish, D. 1996. Ancient whales, sea serpents and nessies part 2: theorising on survival. Animals & Men 10, 13-21.
Vilstrup, J. T., Ho, S. Y., Foote, A. D., Morin, P. A., Kreb, D., Krützen, M., Parra, G. J., Robertson, K. M., de Stephanis, R., Verborgh, P., Willerslev, E., Orlando, L. & Gilbert, M. T. P. 2011. Mitogenomic phylogenetic analyses of the Delphinidae with an emphasis on the Globicephalinae. BMC Evolutionary Biology 11: 65.